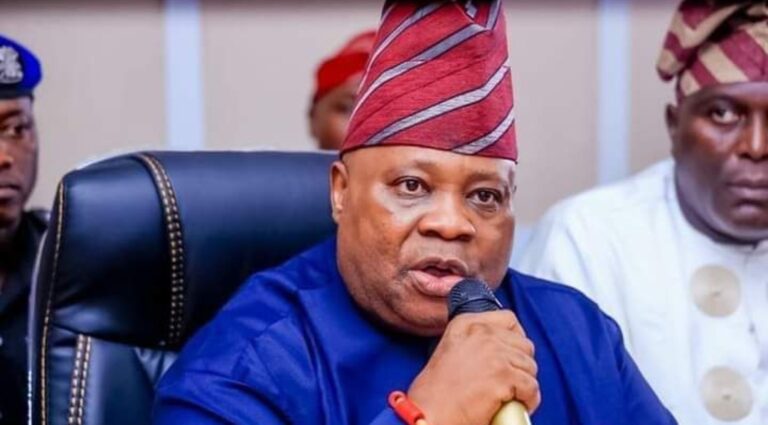
Panic has gripped both the Peoples Democratic Party and the All Progressives Congress in Osun State amid reports that Governor Ademola Adeleke may be planning to leave the PDP for the APC.
According to findings by The Punch, several close associates and appointees of the governor confirmed that Adeleke is close to finalising the defection.
The development has unsettled the APC, prompting a protest against Adeleke on Friday. However, in a statement by his spokesperson, Olawale Rasheed, the governor denied having any such intention.
Speculation about Adeleke’s defection began in June after he paid a visit to President Bola Tinubu at his Bourdillon residence in Lagos.
The governor was accompanied by his brother, billionaire businessman Adedeji Adeleke, and his nephew, Afrobeats artist David Adeleke, also known as Davido.
News of the visit was made public in a post on X by Tinubu’s Special Assistant on Social Media, Dada Olusegun.
Although the purpose of the meeting was not disclosed, the release of photos showing Tinubu and his wife in a warm exchange with the Adelekes triggered tension in both the Osun PDP and APC camps.
The rumour gained renewed attention this week following a series of cryptic posts by some of Adeleke’s aides on social media.
Close associates confirm move, APC ticket offer
Insiders in the governor’s cabinet, including a commissioner and two special advisers, told our correspondents that Adeleke had concluded plans to join the APC.
The commissioner, who spoke on condition of anonymity due to the sensitivity of the matter, said Adeleke had briefed some of his allies in his cabinet and the House of Assembly about his defection plan.
“Mr Governor will join the APC, but the official declaration will not be now. His planned defection is a result of political threats, the Federal Government withheld local government funds, and there are emerging threats to the businesses of his billionaire brother, Dr Deji Adeleke. So, there are many things at stake,” he said.
A senior official of the APC in the state also confirmed that the governor was consulting with APC leaders, but said his fate hangs on Tinubu’s move.
“Adeleke has been consulting many APC leaders. He has employed some mercenaries to lobby the President. But Baba Bisi Akande and Oyetola have not consented to his defection. The President will need to convince them before the governor will declare his defection,” the APC official said on Thursday.
In a symbolic move, the Osun PDP Director of Media and Information, Oladele Bamiji, who is also a Senior Special Assistant to Adeleke, posted “On Your Mandate!” on his Facebook timeline around 5 pm on Thursday.
The slogan is synonymous with Tinubu, having originated from his loyalists in Lagos State.
Bamiji’s post triggered reactions from other Facebook users, including APC members kicking against the move.
One of the governor’s special advisers, who also spoke on condition of anonymity due to the sensitivity of the matter, said the governor’s apparent uncertainty over the validity of his second-term ticket in the face of the PDP crisis might have triggered his proposed defection.
“INEC has released the timetable for the 2026 governorship election, and the PDP primary is coming up in September. Who is going to sign Adeleke’s nomination form amid the ongoing crisis in the PDP?
“We are all afraid that whatever happens in the PDP regarding the Osun election may be subject to litigation, which may invalidate the governor’s nomination and victory. That is why the governor wants to leave,” the aide said.
Also subtly confirming the move, another SSA to Adeleke, Olalekan Badmus, tweeted on his X handle on Friday: “After we all agreed to this, the next question is where?
“Governor Adeleke is currently consulting and evaluating all options on the table, including the peculiarities of all current political parties. Reports of imminent arrival at a particular party are at best speculative.”
Amid growing confirmation from the governor’s close associates, The Punch gathered that Tinubu’s Chief of Staff, Femi Gbajabiamila, and members of the President’s immediate family reportedly facilitated Adeleke’s move to the APC.
Adeleke remains in PDP – Spokesman
Reacting to the defection rumour, the spokesperson for the Osun State Government, Rasheed, said Adeleke remained in the PDP and was not considering joining the APC.
In a statement on Thursday, Rasheed quoted Adeleke as saying, “I assure the good people of Osun that I remain part and parcel of the PDP family. I am not defecting to any party.”
He said the governor reaffirmed his commitment to the implementation of his administration’s five-point agenda and urged the public to disregard what he described as “fake news,” while assuring continued delivery of good governance and democratic dividends.
Also reacting, the National Secretary of the APC, Ajibola Basiru, said the party’s national secretariat was unaware of any defection plan by the Osun governor.
In an interview (with Saturday Punch), Basiru said, “The only thing I can say is that I’m not aware of Adeleke’s so-called planned defection as the National Secretary of the party. All other things are hypothetical for now. I cannot be reacting based on social media frenzy!”
Similarly, the spokesperson for the Osun APC, Kola Olabisi, said the party leadership in the state had no knowledge of any move by Adeleke to join their ranks.
“It is still in the realm of speculation. The leadership of the APC in Osun, led by Sooko Tajudeen Lawal, is not aware of the governor’s defection plan,” he said.
When asked whether the party would welcome Adeleke, Olabisi replied, “Only the leadership of the party will speak on that.”
Panic in APC, PDP camps
Despite official denials, there is palpable tension among members of both the APC and PDP in Osun State.
It was gathered that the development has unsettled many APC members, particularly loyalists of former Governor Gboyega Oyetola, who fear that Adeleke’s entry into the APC could jeopardise the chances of their governorship aspirant, Bola Oyebamiji.
On the PDP side, some members have also expressed concern that the party may suffer significant setbacks if Adeleke defects, as the Adeleke dynasty is regarded as the party’s primary financier in Osun State.
It was noted that several APC members took to social media, especially Facebook, to express displeasure over the alleged plan.
A former Special Adviser to ex-Governor Oyetola on Education, Alhaji Jamiu Olawumi, wrote on his Facebook timeline on Thursday, “The Adeleke Challenge! If, as a governor, you have delivered, is it not shameful trying to run away from your own party?”
Another Oyetola loyalist, Adedeji Adebayo, also took to Facebook to criticise APC National Secretary, Basiru, for saying that President Tinubu would determine the APC’s governorship candidate in 2027, rather than speaking out against Adeleke’s rumoured defection.
He wrote, “The Adelekes’ agents in the APC are celebrating, granting media interviews about the phantom defection of the so-called ‘omo-gba-feeder’. Yes, the same omo-gba-feeder. They don’t care if it goes to a dullard since it’s not coming to them. That is the kind of wanton politics they play. Meanwhile, it is what it is: phantom defection. If Obente defects to APC, perhaps it is the APC AISU Chapter.”
‘No automatic ticket for gov’
On Friday, some Osun APC members staged a peaceful protest at the party’s state secretariat in Osogbo, insisting that if Adeleke defects, he should not be given an automatic governorship ticket.
Led by a member of the APC, Taofeek Afolabi, the protesters, mostly youths, said it would be unfair to hand the incumbent governor the party’s ticket without a contest.
“We are members of the All Progressives Congress, and we are here this morning to register our concern over the rumoured defection of Governor Ademola Adeleke to the APC. We are not saying he should not join our party. Adeleke joining the APC will boost our party. He is the current governor, and having him with us will strengthen the party,” Afolabi said.
“However, what we don’t want is the party giving Governor Adeleke an automatic ticket. If he wants to re-contest, he should express interest and contest the gubernatorial ticket with other aspirants.
“There are people who have shown interest in the race already, and we don’t want him to be handed the ticket without a proper contest. That is the only thing we are against. We have no issue with him joining our party,” he added.
PDP, APC chieftains divided
Saturday PUNCH gathered that members of both the PDP and APC remain divided over the governor’s reported defection plan.
While a section of the PDP reportedly supports the move, others have rejected it, insisting they would not follow the governor into another party.
A former Deputy National Publicity Secretary of the PDP, Diran Odeyemi, said realignment was part of politics and that there was nothing wrong with adjusting strategies to win elections.
“Politics is dynamic. It’s not like mathematics, where you get a fixed answer to an equation. It’s about permutation here and there. It’s a game that is played according to situations and circumstances, but with the sole purpose of winning,” Odeyemi said.
“Realignment is key in politics, more so because it is a game of interest. There is nothing wrong with redefining a strategy if it is aimed at winning any contest. As for us in the PDP, Governor Ademola Adeleke’s second term is sacrosanct; the way and manner to go about it is secondary.”
Meanwhile, a chieftain of the APC in Osun and an aide to ex-Governor Oyetola, Jamiu Olawumi, maintained that while party membership is a right, acceptance is not automatic.
“Politics and joining a political party are fundamental human rights. Joining a party is a free entry and free exit. However, in some situations, you cannot just join a political party because there are certain criteria for fresh members. If you’re not fit for it, we might not welcome your overtures,” he said.
Olawumi also dismissed the defection report as speculation.
“The highest hierarchy of the party has not spoken about the defection. Everybody is just reacting to rumours — we’ve had both confirmations and denials. This shouldn’t be given serious attention by serious people. In the APC, we are serious people, and we don’t dwell on this kind of unserious speculation. Let it remain in the realm of rumour,” he added.
We’re not worried—APC aspirants
Some governorship hopefuls in the Osun APC has said the defection rumour is not giving them sleepless nights.
One of them, Dotun Babayemi, said the development did not come as a surprise and would not affect his ambition.
Speaking through his spokesperson, Kayode Oladeji, Babayemi stated that Adeleke’s defection would, in fact, be an addition to the APC.
“We are not worried about Governor Ademola Adeleke or anybody coming into our great party, APC. We all know that democracy is a game of numbers. This means it is becoming clear that our party is poised to win in 2026, and President Tinubu’s victory in the 2027 elections shall be resounding,” he said.
“In the same vein, his joining our party cannot jeopardise my chances. My confidence is based on the amazing support and love being shown to me within and outside the APC, across the state, by both the old and the young.
“As to whether it is right for the governor to dump the PDP for the APC, I am not sure that is the real question — because we don’t know what is chasing him from the PDP,” he added.
Similarly, another governorship hopeful, Akin Ogunbiyi, said he was not surprised by Adeleke’s reported defection plan, declaring that the party would win the next governorship election in the state.
“I am not worried that the current governor is struggling to come to the APC. He is a serving governor, and he can come to the APC. Our party is a winning team, and we can all see what is happening at the federal level — what our father, the President, is doing.
“So, I am not surprised that not only in Osun State, but even across other states, people are declaring for the APC because it is a progressive party,” Ogunbiyi said.
PDP senators to dump party
Meanwhile, Saturday PUNCH has gathered that two PDP senators from Osun State, Adenigba Fadahunsi (Osun East) and Olubiyi Ajagunla (Osun Central), have concluded plans to leave the party.
According to aides, both lawmakers met with President Bola Tinubu at the Aso Rock Villa about a month ago, where the decision regarding their defection was finalised.
One of Ajagunla’s top aides, who spoke on condition of anonymity, said, “Ajagunla will leave the PDP soon, there is no doubt about that. The Adeleke dynasty is not treating him well, and our town, Ila-Orangun, has not benefited from the current administration in terms of infrastructure development.
“People know that Ajagunla has left the PDP; he just hasn’t announced his defection officially,” the aide said.
Credit: The Punch

 BIG STORY5 days ago
BIG STORY5 days ago
 BIG STORY1 day ago
BIG STORY1 day ago
 BIG STORY2 days ago
BIG STORY2 days ago
 BIG STORY5 days ago
BIG STORY5 days ago
 BIG STORY3 days ago
BIG STORY3 days ago
 BIG STORY3 days ago
BIG STORY3 days ago
 BIG STORY3 days ago
BIG STORY3 days ago
 BIG STORY2 days ago
BIG STORY2 days ago